25-01-2013
Keywords: alkali metals; biomass; catalytically active sites; heterogeneous catalysis; manganese oxide
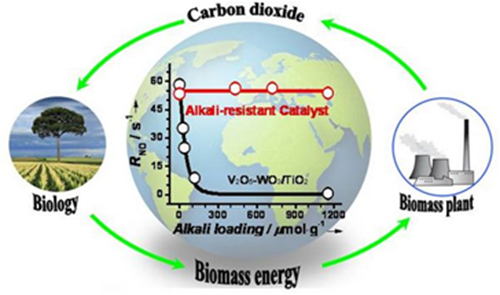
Banish the villains to their own realm: Biomass has gained widespread attention as a renewable energy
source. However, commercial catalysts used in power plants (co-)fuelled by biomass are deactivated by the
alkali-rich flue gas (see graph, black line). In contrast, one of two types of active sites in a promising alkali-
resistant hollandite catalyst traps alkali-metal ions to free up the catalytically active sites for the reduction of
NO by NH3.The research was conducted at the SSRF beamline 14B1.
Zhiwei Huang, Xiao Gu, Wen Wen, Pingping Hu, Michiel Makkee, He Lin, Freek Kapteijn, Xingfu Tang
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 660-664