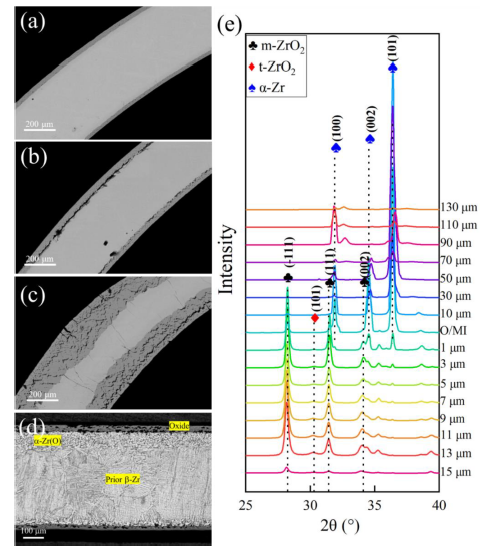
The oxidation behavior of zirconium alloy in high-temperature steam plays a dominant role in the operation of nuclear reactors under accident conditions. Professor Yun Di's team at Xi'an Jiaotong University investigated the effect of Sn on the oxidation behavior of zirconium alloys in high-temperature steam at 1000 °C. The results obtained through TEM, metallographic microscope, and SR-μ-XRD analyses indicate the presence of three layers in the oxidized samples, namely β-Zr, α-Zr(O), and ZrO2. Researchers proposed the mechanism for the transformation of Zr-Sn intermetallic phases into nanovoids based on characterization and computational results.This mechanism provides a new idea to reveal the role of Sn in the oxidation resistance of zirconium alloy under LOCA (Loss-of-Coolant Accident) conditions. The relevant research was published in Acta Materialia under the title “Understanding the oxidation resistance of zirconium alloy at 1000 ℃ based on the formation of a Zr-Sn intermetallic phase and co-precipitation of Sn and Nb”.
附件下载:
