A team led by Professor Xiao Fengshou from Zhejiang University has made significant progress in prolonging the lifespan of catalysts. They employed dealuminated Beta zeolite molecular sieves as carriers and regulated the dynamic evolution of copper nanoparticles during catalytic reactions. This approach effectively eliminated copper particle sintering and controlled the secondary dispersion of already sintered copper nanoparticles, thus significantly extending the catalyst's lifespan. To gain insights into the structural changes of copper particles, the team utilized X-ray absorption spectroscopy techniques at the BL11B beamline of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility. This provided crucial evidence for their analysis. The research paper, titled "Dealuminated Beta zeolite reverses Ostwald ripening for durable copper nanoparticle catalysts," was published in Science in December 2023. This study offers a promising approach to enhancing the durability of copper nanoparticle catalysts, which has the potential to revolutionize various catalytic processes in industrial applications.
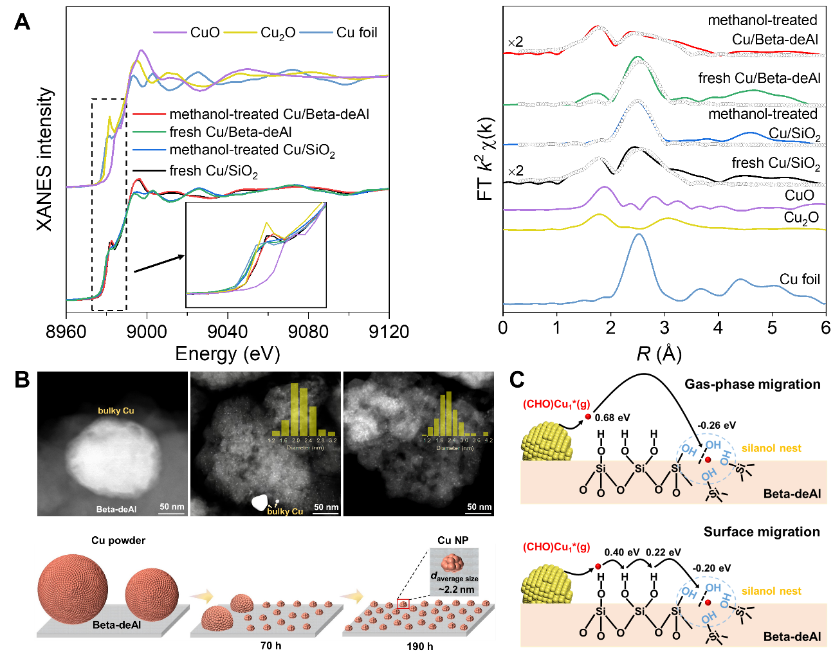
Figure 1. Illustration of the process of methanol-atmosphere-induced migration and dispersion of atoms from copper particles and bulk copper surfaces onto the zeolite molecular sieve surface.
Related Paper:
Liu, L.; Lu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ruettinger, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Lou, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, X.; et al. Dealuminated Beta zeolite reverses Ostwald ripening for durable copper nanoparticle catalysts. Science 2024, 383 (6678), 94-101. DOI: 10.1126/science.adj1962. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adj1962
附件下载:
